CLASS-10 | CHAPTER-6 | LIFE PROCESS
STRUCTURE OF A LEAF
The structure of leaf can be discussed as:-
(a)EXTERNAL STRUCTURE
The external structure of leaf consist of lamina, veins, mid-rib and petiole.
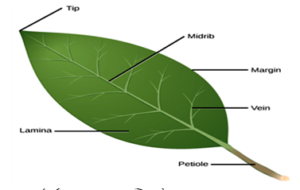
(i)Lamina: It is a flat, thin and large surface area of the leaf. It is responsible for the absorption of the sunlight.
(ii) Vein: These are the vascular structures on the leaf which supply water throughout its surface.
(iii) Mid-rib: It is the mid line on the leaf which divide it into two equal parts.
(iv) Petiole :It is the stalk of the leaf it is responsible to attach the leaf to the stem.
(b)INTERNAL STRUCTURE
Internal structure of leaf consist of epidermis and stomata.
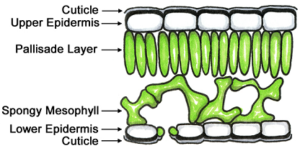
(i) EPIDERMIS-It is the uppermost layer of the leaf. It consist of two parts. They are upper epidermis and lower epidermis.
- Upper Epidermis- It is the single layer of transparent cells with no chlorophyll/ chloroplast known as cutile. It prevent excess loss of water during transpiration.
- Lower Epidermis-Lower Epidermis consist of stomata and help in the exchange of gases.
(ii)STOMATA
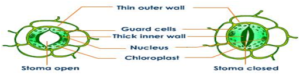
- The tiny pores present on the leaves through which exchange of gases takes place. Each stomata has a pair of guard cell which control opening and closing of stomatal pores.
- When water concentration in outside medium is more than the water concentration inside the guard cells then water enters into the guard cells due to which it swells and the pores open.
- When water concentration in outside medium is less than the water concentration inside the guard cells then water moves outside the guard cells due to which it shrinks and the pores closes.
FUNCTIONS OF STOMATA
There are two main functions of stomata. They are
- (i) Exchange of gases
- (ii) Loss of excess water through transpiration.
Answer the following questions in comment box
- What is the function of Lemina?
- Write any two functions of stomata?
- What is cutile in the structure of leaf.