CLASS-10 CHAPTER-7
CONTROLS AND COORDINATION
STIMULI
Any change in the environment to which living organisms respond is called stimuli. Eg: Hotness, coldness, smell, light, taste touch, pressure, gravity etc.
Note-Living organisms respond to a stimuli in the form of body movements.
COORDINATION
For a proper response to stimuli, many organs in the body work together. The working together of various organs in an organism to produce a proper response to stimuli is called coordination.
- In animals, control and coordination is done by nervous system and endocrine glands.
- In plants , control and coordination is done by plant hormones or phytohormones.
COORDINATION IN ANIMALS
In animals, control and coordination is done by nervous system and endocrine glands
HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM
The human nervous system consist of brain, spinal cord and nerves. The human nervous system consist of two parts.
(i) Central nervous system.
(ii) Peripheral nervous system.
(i) CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
The central nervous system consist of brain and spinal cord.
(ii)PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
The peripheral nervous system consist of cranial nerve(arising from brain) and the spinal nerves( arising from spinal cord).
NERVE CELL(Neuron)
Neuron is the structural and functional unit of nervous system which is composed of the following main parts.
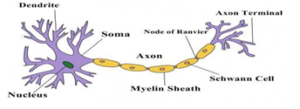
(i) CELL BODY OR CYTON: Neuron has a cell body containing nucleus and cytoplasm and also known as cyton.
(ii)DENDRITES:A neuron has several hair like structures called dendrites. Dendrites are responsible to receive stimuli.
(iii)AXON: A neuron has a long fibrous part called axon. Axon is covered with a protective covering called Myelin Sheath. It is responsible to carry impulses from cell body to nerve ending.
(iv) NERVE ENDING: At the end of the axon, there are some another hair like structures called nerve ending. They are responsible for releasing neurotransmitter which help in the transmission of nerve impulse.
(iv) SYNAPSE:A small gap between the neurons where nerve impulse passes from one neuron to another is called synapse.
LIMITATIONS OF ELECTRICAL IMPULSE
- The electrical impulse will reach only those cells that are connected by nervous tissues
- Once an electrical impulse is generated in a cell and transmitted, the cell will take some time to reset its mechanism before it can generate and transmit a new impulse.
TYPE OF NEURON
There are mainly three types of neuron
- Sensory Neuron
- Motor Neuron
- Relay Neuron
1.SENSORY NEURON
It is responsible to transmit information from receptor to spinal cord or brain.
2.MOTOR NEURON
It is responsible to transmit information from brain or spinal cord to effectors.
3.RELAY NEURON
It is responsible to transmit information between sensory and motor neuron and commonly found in brain and spinal cord.
REFLEX ACTION
Reflex action is a sudden, unconscious and involuntary response to stimuli. For eg: We suddenly withdraw our hand if we touch a hot object.
In this reflex action, the nerve in the skin (receptors) detect the heat and passes the message through the sensory nerve to spinal cord or brain then the information is passes through motor nerve to muscles(effectors) of the hand and then we withdraw our hand.
REFLEX ARC
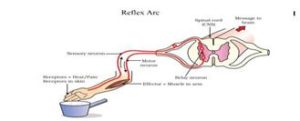
The pathway of a reflex action is called a reflex arc. In a reflex arc, stimuli is received by receptors and passes it to spinal cord with the help of sensory nerve. From the spinal cord information is passes through motor nerve to effectors for a proper response.
ADVANTAGES OF REFLEX ACTION
- It reduces the overloading of brain.
- It increases the chance of survival of an organism.
- It enables an organism for immediate response to harmful stimuli.
BRAIN
The brain is the main coordinating centre of the body which enables us to think and take decision. It is protected by cranium. It is covered by three membrane filled with a fluid called cerebrospinal which protect the brain from shock. The brain has three main parts. They are
(i) Forebrain
(ii) Mid Brain
(iii) Hind brain
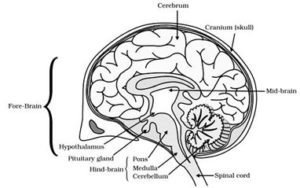
(i) FORE BRAIN
It consist of the cerebrum and olfactory lobes. It is the thinking part of the brain and controls voluntary action. It controls touch, smell, hearing, taste and mental activities like learning and emotions.
(ii) MID BRAIN
It controls involuntary actions and reflex movements of head, neck, eyes etc. it is also responsible to connect forebrain and hind brain.
(iii) HIND BRAIN
It consists of cerebellum, pons and medulla.
Cerebellum: It controls body movements and body postures.
Pons: It controls the respiration.
Medulla:It controls heart beat, blood pressure , coughing, sneezing, vomiting etc.
SPINAL CORD
The spinal cord is a vertebral column. It has 31 pairs of spinal nerves. It carries messages to and from the brain. It also controls reflex action.
STRUCTURE OF SPINAL CORD
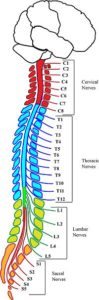
1) Spinal cord extends from the back of the hind brain (medulla oblongata) to the back of the stomach or lumbar region.
2) It is cylindrical in shape. It passes through the neural canal of the vertebral column.
3) The white matter is towards periphery, while grey matter is towards the centre of
the spinal cord. . . ’
4) In the cross-section, grey matter of the spinal cord is in the form of ‘H’ and it is called horn.
5) In the middle of the grey matter of the spinal cord, there is a canal called spinal canal which is filled with Cerebro-spinal Fluid.
6) From the sides of spinal cord 31 pairs of nerves arise and supply branches to various parts of the body.
FUNCTION OF SPINAL CORD
Function of spinal cord is receiving and sending information from brain to various parts and from various parts to brain. And it also helps in reflex actions.
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
It consist of cranial nerves , spinal nerves and visceral nerves.
1. Cranial Nerves: These are the nerves which arise from brain and spread throughout the head.
2.Spinal Nerves: These are the nerves which arise from spinal cord and spread throughout the body(except head)
3.Viceral Nerves: Theses are the special cord and are connected to internal organs of the body.
Q: What is difference between reflex action and walking.
Reflex Action | Walking |
1. It is a sudden and involuntary response to a stimuli. | 1.It is acquired through learning and a voluntary a response. |
2. It is controlled by the spinal cord | 2. It is controlled by the brain. |
3. It increases the chance of survival of an organism. | 3. It is connected with locomotion |
4. Its intensity cannot be changed. | 4. Its intensity can be changed. |
HORMONES IN ANIMALS
Hormones are chemical substances secreted by endocrine glands in one part of the body and are carried by blood to the site of action. These hormones act on a specific organ’s cell has a specific protein molecule called receptor. The receptor can recognize and pick out the specific hormone capable of acting in cell.
GLANDS
A gland may be a cell, a tissue or an organ which secrete useful chemical compounds required for a particular function.
There are two types of glands.
- Endocrine glands
- Exocrine glands
1.ENDOCRINE GLANDS
These are the glands which are not have a duct and pass their secretion into blood to transport to the site of action.
Eg- Pituitary gland, Thyroid gland, Adrenal gland, testes etc.
2.EXOCRINE GLANDS
These are the glands which have a ducts for discharging their secretion.
Eg- Salivary gland, Gastric gland, liver etc.
SOME IMPORTANT GLANDS , THEIR LOCATION AND FUNCTIONS
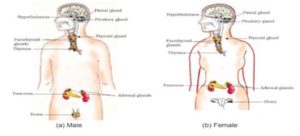
1.ADRENAL GLAND
These glands are present in pair and are situated on the upper side of each kidney. It secrete a hormone adrenalin and known as emergency hormone. In normal situation these hormones are secreted in small amount, however when a person faces stress, danger, they secretes hormones in large amount.
Functions
1. it increases the heart beat to supply more oxygen to muscles.
2. It regulate the blood pressure.
3. It controls increasing in breathing rate due to contraction of diaphragm and rib muscles.
2.THYROID GLAND
It is the largest endocrine gland in our body. It is situated in neck region. It secretes hormone thyroxine. Iodine is essential for the synthesis of thyroxine.
Function
(i) It controls the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, proteins in our body.
(ii) It regulate the rate of oxidation.
Note- It is advised to use iodine salt in food because deficiency of iodine in diet causes Goitre. It causes enlargement of thyroid gland. Swollen neck is one of the symptoms.
3.PITUTARY GLAND
It is present just below the brain. It is small, red-grey pea shaped gland. It secrete growth hormone. Improper secretion of growth hormones can causes dwarfism(due to deficiency of growth hormones) and Gigantism(due to excess secretion of growth hormones).
4.TESTES
In males, a pair of testes is present. They secrete male sex hormone Testosterone which is responsible for the secondary sexual growth in males.
5.OVARIES
In females, a pair off ovaries is present. They secrete female sex hormones Estrogen and Progesterone.
- Estrogen helps in the development of secondary sexual characters in females.
- Progesterone helps in maintaining pregnancy
6. PANCREAS
It lie below the stomach. It secretes pancreatic juice and two hormones Insulin and Glucagon(Glucagen).
(i)Insulin: It reduces the blood sugar or glucose level by the oxidation of sugar present in blood. Deficiency of this hormone causes diabetes.
(ii)Glucagon: It increases the concentration of glucose in blood stream. It causes the liver to convert stored glucagon into glucose, which is released in blood stream.
7. PINEAL GLAND
It is located near the centre of the brain and produces the hormone Melatonin. It controls the wake and sleep patterns.
8.HYPOTHALAMUS
It is neuro- endocrine part of the brain. It links the nervous system and the endocrine system through the pituitary gland. It secrete hormones Dopamine & Stomatostanin .
9.THYMUS GLAND
It is located in front of the heart in the upper part of the sternum. It produces the hormone Thymosine and help to attain maturity.
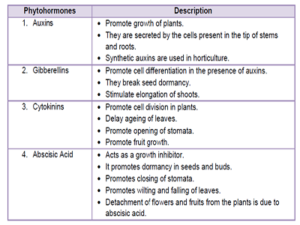
HORMONES IN PLANTS
Control and coordination in plants takes place by plant hormones or phytohormones.
MOVEMENT IN PLANTS
There are two types of tropic movement
(i)Tropic Movements
(ii)Nastic Movements
(i)TROPIC MOVEMENT
These are directional movements towards or away the stimuli and it depends on growth. There are different types of tropic movements.
(a)Phototropism
(b)Geotropism
(c) Chemotropism
(d) Hydrotropism
(e) Thigmotropism
(a) PHOTOTROPISM: It is the movement of plants in response to light.
- If it is towards light, it is called positive phototropism. Eg: Movement of shoot towards light.
- If it is away the light, it is called negative phototropism. Eg: movement of root away the light.
(b)GEOTROPISM: It is the movement of plants in response to gravity.
- If it is towards gravity, it is called positive geotropism. Eg: Downward growth of roots.
- If it is away from gravity, it is called negative geotropism. Eg: Upward growth of shoot.
(c)CHEMOTROPISM: It is the movement of plant in response to chemical stimuli. Eg- Growth of pollen tube towards the ovule.
(d) HYDROTROPISM: It is the movement of plants in response to water.
- If it is toward water, it is called positive hydrotropism. Eg- Downward growth in aquatic plants.
- If it is away the water, it is called negative hydrotropism. Eg-Upward growth in aquatic plants.
(e) THIGMOTROPISM: It is the movement of plant part in response to touch. Such movements are seen in tendrils of climbers.
(ii).NASTIC MOVEMENTS
These are non- directional movements which are neither towards or away the Stimuli. Nastic movement does not depends on the growth of the plants.
Eg: If we touch the leaves of touch-me-not plant, its leaves fold up immediately due to change in amount of water in the leaves. Depending on the amount of water in the leaves, they swell or shrink.
FEEDBACK MECHANISM
The feedback mechanism regulates the timing and amount of hormone to be secreted.
For example: If a person has more sugar in his blood then it is detected by the cells of pancreas. As a result, more insulin will be secreted to oxidize the sugar. As blood sugar level falls, insulin secretion is reduced.
HAVE A GOOD DAY…..