CLASS-10
CHAPTER-15
OUR ENVIRONMENT
OUR ENVIRONMENT
The environment includes our physical surrounding like air, water bodies, soil and all organisms such as plants and animals.


WASTE MATERIALS PRODUCED BY HUMAN ACTIVITIES
Human activities produce a lot of waste materials which are thrown away into the environment. These wastes causes air, water and soil pollution. There are two types of waste materials.
(a)Biodegradable waste
(b)Non-biodegradable waste
(a)BIODEGRADABLE WASTES: These are the wastes which are easily decomposed by microorganisms into harmless substances within a very short period of time .Eg: waste produced by vegetables, fruits, paper, cattle dung etc.
(b) NON-BIODEGRADABLE WASTE: These are the wastes which are not easily decompose by microorganisms or take very long time to decompose. Eg: Polythene bags, plastics, synthetic fibres etc.
Q:What are the differences between biodegradable and non biodegradable waste?
Ans
| BIODEGRADABLE WASTE | NON BIODEGRADABLE WASTE |
| 1.These can be broken down into simple, non-poisionous substances by the action of micro-organisms in nature | 1.These cannot be broken down into simple, non-poisionous substances by the action of micro-organisms in nature |
| 2. They can be recycled naturally as well as by man and their products do not pollute the environment. | 2. They cannot be recycled naturally as well as by man and their products cause environmental pollution |
| 3. These wastes are made up of natural ingredients. | 3. These wastes are made up of synthetic materials |
| 4. They do not disturb the ecological balance in nature. | 4. Most of the time they disturb the ecological balance in nature. |
| 5. They can produce useful products after biodegradation | 5. They remain unchanged chemically as they are non-biodegradable |
| 6. They produce fowl smell due to biodegradation. | 6. They do not produce fowl smell because they do not degrade |
| 7. Eg: waste produced by vegetables, fruits, paper, cattle dung etc. | 7. Eg: Polythene bags, plastics, synthetic fibres etc. |
ECOSYSTEM
An ecosystem consist of all the living organisms in an area along with the non living components and their interaction. There are two types of ecosystem.
(a) Natural Ecosystem (b) Artificial Ecosystem
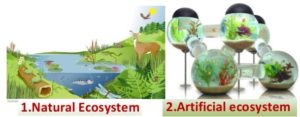
(a)NATURAL ECOSYSTEM: The ecosystems given by nature are known as natural ecosystem. Eg: Forests, desert, grasslands, mountains, ponds, lake, rivers, oceans etc.
(b)ARTIFICIAL ECOSYSTEM: The ecosystems prepared by men are known as artificial ecosystem. Eg: Gardens, parks, aquarium, zoo etc.
COMPONENTS OF ECOSYSTEM
An ecosystem consist of two main components. They are of two main components. They are biotic and abiotic components.
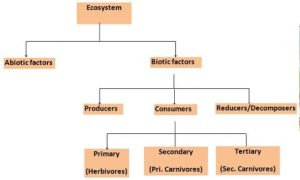
(a)BIOTIC COMPONENTS: These are the living components of an ecosystem like plants, animals and microorganisms. They consist of producers , consumers and decomposers.
- Producers: These are green plants which are produced by photosynthesis.
- Consumers: These are herbivores which get their food directly from plants, carnivores which gets their food from animals and Omnivores which get their food from both plants and animals.
- Decomposers:These are the microorganisms which decompose complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances in the soil which again used by plants.
(b)ABIOTIC COMPONENTS: These are the non living components of ecosystem. Eg: air, water, soil , minerals, sunlight etc.
FOOD CHAIN
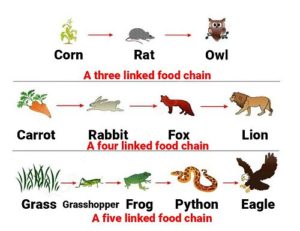
Food chain is the flow of energy(food) from one organism to the next and to the next and soon. They usually starts with producers(plants) and end with a carnivores. In a food chain an organism gets food from a group of organisms.
FOOD WEB
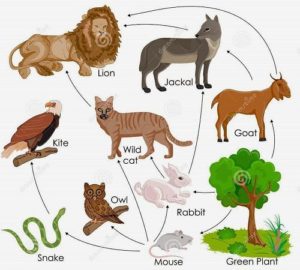
A food web is a group of several interconnected food chains. In a food web an organism gets food from more than one group of organisms.
TROPIC LEVEL
Each step in food chain where transfer of energy takes place is called tropic level.
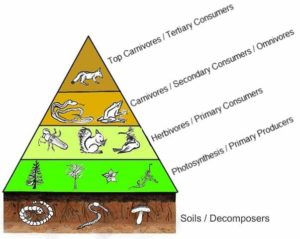
- The first tropic level consist of producers.
- The second tropic level consist of primary consumer.
- The third tropic level consist of secondary consumer.
- The fourth tropic level consist of tertiary consumer.
Since the transfer of energy decreases at every tropic level, therefore number of tropic levels are limited and do not exceed four or five level.
ENERGY FLOW IN TROPIC LEVEL
As we know green plants can absorb about 1% of the solar energy falling on the leaves and store it as energy during photosynthesis. During the transfer of energy from one tropic level to the next 90% of energy is lost in the environment and only 10% energy is transfer to the next tropic level. This law is known as 10% law of energy.
BIOLOGICAL MAGNIFICATION (BIOMAGNIFICATION)
Pesticides and insecticides used in crops are washed down .into the soil. From soil these are absorbed by plants
along with water and minerals and thus, they enter the food chain. While consuming the crops, human
beings also consume these pesticides which get accumulated in our bodies. This phenomenon is known as biological magnification.
OZONE LAYER
An Ozone Molecule(O3) contain three atoms of the oxygen. At higher level in the atmosphere the UV radiation splits some oxygen molecules(O2) into free oxygen atoms(O). These oxygen atoms are combine with oxygen molecule(O2) to form Ozone molecule(O3). These ozone molecules are combine to form ozone layer It is a highly poisonous.
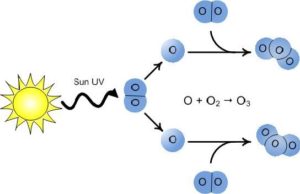
Ozone layer is present in the higher layers of atmosphere protect the earth from harmful ultraviolet radiations which can cause skin cancer in human being.
OZONE LAYER DEPLETION
Ozone layer is being damaged by the use of chemicals like Chloro-fluro Carbon (CFC’s) used in refrigerators and fire extinguisher. This process of damaging of ozone layer is called ozone layer depletion.
So the use of CFC’s is now being reduced to protect the Ozone layer.
Q: How can we manage the garbage we produce?
Ans: The household waste are called garbage. Some of the garbage are biodegradable and some are non biodegradable. Garbage can pollute the air, water soil etc.
Some of the methods of garbage disposal are
- Land Fills
- Recycling
- Production of manure and biogas.
- Preparation of compost
- Incineration
- Sewage treatment