PLASMOLYSIS
The word Plasmolysis was generally derived from a Latin and Greek word plasma – The mould and lusis meaning loosening.
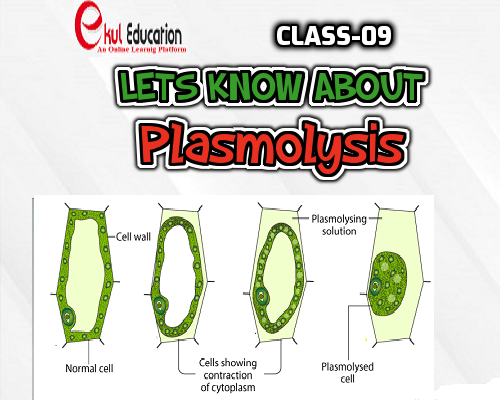
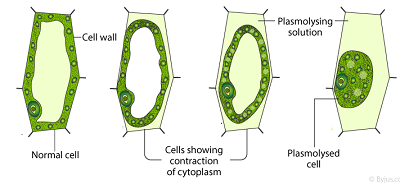
Plasmolysis is defined as the process of contraction or shrinkage of the protoplasm of a plant cell and is caused due to the loss of water in the cell. Plasmolysis is an example of the process osmosis and rarely occurs in nature.
EXAMPLES OF OSMOSIS
- Shrinkage of vegetables in hypertonic conditions.
- Blood cell shrinks when they are placed in the hypertonic conditions.
- When more amount of salt is added as the preservatives for food like jams, jellies, and pickles. The cells lose water due to higher concentration outside and become less conducive to support the growth of microorganisms.
TYPES OF PLASMOLYSIS
On the basis of the final structure of the cytoplasm, there are mainly two types of plasmolysis.
- Concave Plasmolysis
- Convex Plasmolysis
CONCAVE PLASMOLYSIS
During the concave plasmolysis, both the cell membrane and protoplasm shrink away and begins to detach from the cell wall, which is caused due to the loss of water. Concave plasmolysis is a reversible process and it can be revised by placing the cell in a hypotonic solution, which helps calls to regain the water back into the cell.
CONVEX PLASMOLYSIS
During the convex plasmolysis, both the cell membrane and protoplasm lose so much water that they completely get detach from the cell wall. Later, the cell wall collapses and results in the destruction of the cell. Similar to concave plasmolysis, convex plasmolysis cannot be reversed, and this happens when a plant wilts and dies from lack of water. This type of plasmolysis is more complicated compared to convex plasmolysis.
QUESTIONS FOR SELF EVALUATION
- What happen when a cell is placed in hypertonic solution?
- What happen when a cell is placed in hypotonic solution?
- What is plasmolysis?
- …………….plasmolysis cannot be reversed.
PLEASE GIVE YOUR VALUABLE REVIEW IN COMMENT BOX
HAVE A GOOD DAY