CLASS-10
CHAPTER-2
ACIDS, BASIS AND SALTS
On the bases of Chemical properties compounds can be classified as Acids, Bases and Salts
ACIDS
The substances that give H+ ions in aqueous solutions are known as acids. Acids are sour in taste and turn blue litmus to red.
Eg :Sulphuric acid (H2SO4), Acetic acid(CH3COOH), Nitric acid(HNO3), hydrochloric acid(HCl) etc
CLASSIFICATION OF ACIDS
1. ON THE BASIS OF SOURCE: On the basis of sources , acids are classified as
(i)Inorganic acids or mineral acids
(i)Organic and edible acids
(i)INORGANIC ACIDS OR MINERAL ACIDS: The acids which are prepared from minerals present in earth crust are known as inorganic acids or mineral acids.
Eg :Sulphuric acid (H2SO4), Nitric acid(HNO3), hydrochloric acid(HCl) etc
(ii)ORGANIC ACIDS OR EDIBLE ACIDS: The acids which are produced by plants and animals are known as organic acids or edible acids.
Eg: Some of the organic acids and their sources are as follows
|
ACID |
SOURCE |
|
1. Acetic Acid |
Vinegar |
|
2. Citric Acid |
Lemon, Orange and grapes |
|
3. Maleic Acid |
Apple |
|
4. Lactic acid |
Curd |
|
5. Tartaric acid |
Tamarind |
|
6. Oxalic Acid |
Tomato |
|
7. Methanoic acid or Formic acid |
Ant Sting |
2. ON THE BASIS OF IONIZATION: On the basis of ionization, acids are classified as
(i)Strong Acids
(ii)Weak Acids
(i)STRONG ACIDS: The acids which completely dissociate H+ ions in aqueous solution are called strong acids.Eg :Sulphuric acid (H2SO4), Nitric acid(HNO3), hydrochloric acid(HCl) etc
(ii)WEAK ACIDS: The acids which partially dissociate H+ ions in aqueous solution are called weak acids.
Eg: Acetic acid(CH3COOH), Carbonic acid(H2CO3) etc.
Note-All the mineral acids except carbonic acid are strong acids
Q: Identify the following acids as strong orWeak acid.
|
Acids |
Strong/Weak |
|
1. Hydrochloric Acid |
Strong |
|
2. Sulphuric acid |
Strong |
|
3. Nitric acid |
Strong |
|
4. Acetic acid |
Weak |
|
5. Phosphoric acid |
Strong |
|
6. Oxalic acid |
Weak |
|
7. Carbonic acid |
Weak |
3. ON THE BASIS OF CONCENTRATION: On the basis of concentration, acids are classified as
(i)Dilute acids
(ii)Concentrated acids
(i)DILUTE ACIDS: If in an aqueous solution, concentration of acid is low then it is called dilute solution.
(ii)CONCENTRATED ACID: If in an aqueous solution, concentration of acid is high then it is called concentrated solution.
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF ACIDS
1. Acids are sour in taste.
2. They turn blue litmus to red.
3. They are electrolyte.( They can conduct electricity).
4. They are corrosive in nature( they can cause corrosion).
5. They are soluble in water.
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF ACIDS
1.REACTION WITH METALS: Acids react with metal to form salt and hydrogen gas.
Metal + acid Salt + Hydrogen gas
Examples (i) Zn +H2SO4 ZnSO4 + H2
(ii) Fe + HCl FeCl3 + H2
(iii) Na + CH3COOH CH3COONa + H2
2. REACTION WITH METAL OXIDES: Acidsreact with metal oxide to form salt and water
Metal Oxide + acid Salt + Water
Examples (i) Al2O3 + 2HCl Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2O
(ii) MgO + 2HCl MgCl2 + 2H2O
(iii) ZnO + 2 CH3COOH (CH3COO)2Zn + H2O
3. REACTION WITH METAL CARBONATE OR METAL BICARBONATE
Metal Carbonate/ Metal bicarbonate + acid Salt + Water + CO2
Examples (i) CaCO3 + 2HCl CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
(ii) Ca(HCO3)2 + 2HCl CaCl2 + 2H2O + 2CO2
(iii) Na2CO3 + 2HCl 2NaCl+ H2O + CO2
(iv) NaHCO3+HCl NaCl + H2O + CO2
Q:Why hydrogen gas is not evolved when an active metal react with Nitric acid?
Ans: Hydrogen gas is not evolved when an active metal react with nitric acid because nitric acid is strong oxidizing agent. It oxidizes hydrogen gas into water and itself gets reduced.
11Na + 14 HNO3 11NaNO3 + N2O + NO + 7H2O
- REACTION WITH BASES: Acids react with base to form salt and water. In this reaction acid and base neutralize each other. Therefore, this reaction is known as neutralization reaction.
Acid + Base Salt + Water
Examples: (i) NaOH + HCL NaCl + H2O
(ii)H2SO4 + KOH K2SO4 + H2O
(iii) CH3COOH + Ca(OH)2 (CH3COO)2Ca
TEST FOR HYDROGEN
When a burning candle comes in contact with H2 gas then it burns with pop –up sound.
TEST FOR CO2
- When a burning candle comes in contact with CO2 gas then it will extinguish.
- When CO2 gas is passed through lime water then it become milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate (ppt).
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 CaCO3 + H2O
Calcium carbonate
(whiteppt)
Q: What happen when CO2 gas is passed in lime water? And also what happen when it is passed in excess?
Ans: When CO2 gas is passed through lime water then it become milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate (ppt).
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 CaCO3 + H2O
Calcium carbonate
(whiteppt)
When CO2 is passed in excess then mikliness disappear due to the formation of calcium bicarbonate which is soluble in water.
CaCO3 + H2O + CO2 Ca(HCO3)
Calcium bicarbonate
Note:Marble , limestone, Egg shell all are the different form of calcium carbonate.
USES OF ACIDS
- ACETIC ACID(Vinegar): Acetic acid is used to preserve pickles and Chinese food.
- HYDROCHLORIC ACID: In stomach, hydrochloric acid is released which make the medium acidic and kills the bacteria.
- CARBONIC ACID: Carbonic acid is used in cold drinks.
- SODIUM BENZOATE(NaC7H5O2): It is used to preserve cold drinks and food stuff.
- OXALIC ACID: oxalic acid is used to remove ink and rust stain from cloths.
- ASCORBIC ACID(C6H8O8): It is present in orange, amla, grapes etc. It prevent us from Scurvy.
- SULPHURIC ACID: It is used in the manufacturing of fertilizers, dyes, detergents, paints and other acids like HNO3 and HCl.
- NITRIC ACID: It is used in the manufacturing of dynamites and explosives.
Q: What precautions should be taken while handling acids in laboratory?
Ans: Since concentrated acids are very dangerous and can harm us therefore, we should taken the following precautions while dealing with acids when dealing with acids.
- Always wear a lab coat so that concentrated acids may not come in contact with ours cloth.
- The acids must always be added slowly to water along with the walls of the vessel.
- Use goggles for the protection of eyes.
- Never try to touch or taste an acid.
- Water should not be added to concentrated acids because this can break the glass container due to excessive heating and may cause the mixture to splash out and causes burn.
BASES
The substances that gives hydroxide ions(OH–) in aqueous solution are called bases. They are bitter in taste ,soapy in touch and turns red litmus to blue.
Eg: Sodium Hydroxide(NaOH), Potassium Hydroxide(KOH), Magnesium hydroxide(Mg(OH)2) etc.
STRONG AND WEAK BASES
- STRONG BASES: The bases which completely dissociate hydroxide ions (OH–) in aqueous solution are called strong bases.
Eg: Sodium hydroxide(NaOH), Potassium hydroxide(KOH) etc
- WEAK BASES: The bases which partially dissociate hydroxide(OH-) ions in aqueous solution are called weak bases.
Eg: Calcium hydroxide(Ca(OH2)), magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2), Ammonium hydroxide NH4OH etc.
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF BASES
- Bases are bitter in taste.
- They are soapy in touch.
- They turn red litmus to blue.
- Bases are electrolyte( The can conduct electricity in aqueous solution).
Q: What are alkalis ?
Ans: Water soluble bases are called alkalis for example NaOH, Ca(OH)2 etc.
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF BASES
1.REACTION WITH METALS: Bases react with non metals to form salt and hydrogen gas.
Metal + Bases Salt + Hydrogen gas
Examples: (i) Zn +NaOH Na2ZnO2+ H2
(ii) Al + NaOH NaAlO2 + H2
2. REACTION WITH NON-METALIC OXIDE: Bases react with non metallic oxides to form salt and water.
Non–metallic oxide + Bases Salt + Water
Examples: (i) CO2 + 2NaOH Na2CO3 + H2O
(ii) CO2 + Ca(OH)2 CaCO3 + H2O
DILUTION
Dilution is the process of mixing of acids or base slowly in water, it results in the decreases the concentration of H+ or OH‑ions per unit volume. Now the acid or base is said to be diluted.

INDICATORS
Indicators are the substances which are used to identify whether a given solution is acid or base. Indicators give different colour or smell in acidic and basic medium.
TYPES OF INDICATORS: There are three types of indicators
- Natural indicators
- Synthetic Indicators
- Olfactory indicators
- NATURAL INDICATORS: The indicators which are found in nature(Plants and animals) are called Natural Indicators. Some natural indicators with their colour in acidic and basic medium are-
|
INDICATORS |
Colours in Acids |
Colours in base |
|
1. Litmus |
Red |
Blue |
|
2. Red Cabbage |
Red |
Green |
|
3. Turmeric |
Yellow |
Reddish- Brown |
|
4.Flower Hydrandea |
Blue |
Pink |
- SYNTHETIC INDICATORS: The indicators which are synthesized in laboratory or industries are called synthetic indicators. Some synthetic indicators with their colour in acidic and basic medium are-
|
INDICATORS |
Colours in Acids |
Colours in base |
|
1. Methyle Orange |
Red |
Yellow |
|
2. Phenolphthalein |
Colourless |
Pink |
- OLFACTORY INDICATORS-The substances which give different smell in acidic and basic medium are called olfactory indicators. Eg- Onion, Cloves,Vanilla etc.
LITMUS SOLUTION
It is a purple coloured dye extracted from lichen plant. It is commonly as an acid base indicator.
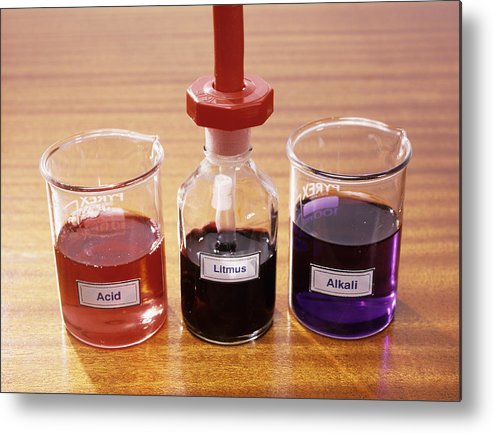

🡪When a small amount of acid is added to litmus solution, it turns into red.
🡪When small amount of base is added to litmus solution, it turns into blue.
USES OF BASES
- Sodium bicarbonate is used for cooking purpose.
- Sodium hydroxide (Caustic soda) is used as drain cleaner.
- Magnesium hydroxide is used as antacid.
PH SCALE
PH stands for potenz of hydrogen(power of hydrogen). In 1909, Sorenson gave a scale to measure the strength of an acid or a base on the basis of the concentration of hydrogen ions present in a solution.
🡪 Higher the PH of a solution, lower the concentration of H+ ions.
🡪 Lower the PH of a solution, higher the concentration of H+ ions
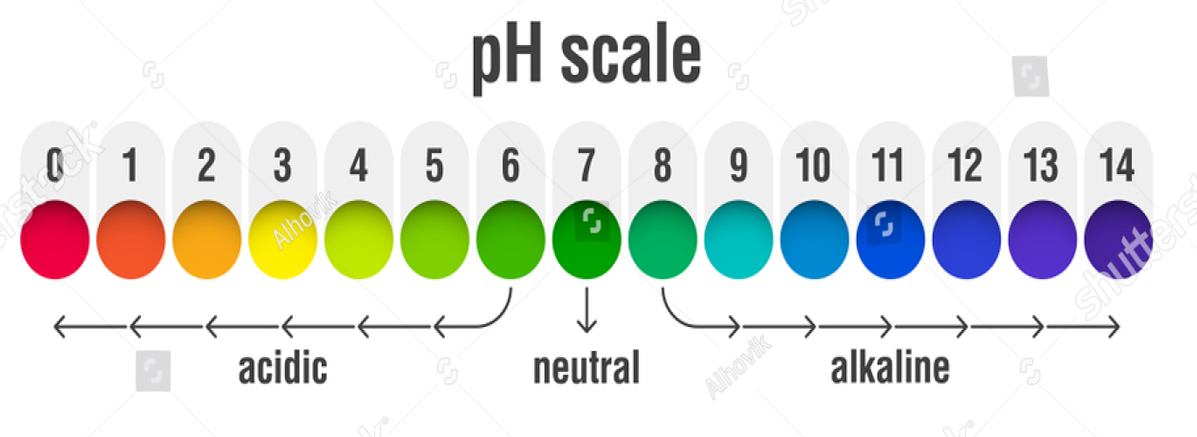
RANGE OF pH
- In acidic solution: 0-7
- In basic solution : 7-14
- In Neutral solution(Salts): 7
IMPORTANCE OF pH IN DAILY LIFE
Importance of PH in everyday life can be understand with the help of following examples
- PLANT AND ANIMALS ARE pH SENSITIVE: The body of plants and animals are pH work within a pH range of 7.0 to 7.8 when pH of river water goes below 5.6 due to acid rain then aquatic life feel difficulty in their survival.
- pH OF SOIL: Different crops need different pH in soil to grow. therefore, it is necessary to know the pH of soil before growing any crop.
- pH IN OUR DIGESTIVE SYSTEM:Hydrochloric acid present in our stomach help in digestion of food. Excess secretion of hydrochloric acid leads to decreases in pH value of digestive system which causes stomach pain and irritation. In this case antacids are used to increase the pH of our digestive system and reduce the effect of acids.
- pH CHANGE LEADS TO TOOTH DECAY: The normal pH of our mouth is 5.5. If the pH inside the mouth decrease below 5.5 due to acid forming bacteria present in our mouth. Then it leads to tooth decay.
- When an insect like honey bee or ant bite, they inject an acid (Methanoic acid) in the skin that causes pain and irritation. In this case, a mild base like baking soda is applied on affected area to get relief.
Q:Under what condition the do you think a farmer would treat the soil of his field with Quick lime(calcium oxide)/ Slaked lime(Calcium hydroxide) /Chalk(Calcium carbonate)?
Ans:If the soil is acidic and improper for cultivation , then to increases the basic nature of the soil, farmer would treat the soil of his field with Quick lime(calcium oxide)/ Slaked lime(Calcium hydroxide) /Chalk(Calcium carbonate)
Chemical name: Sodium Hydroxide Chemical formula: NaOH
Formation:Sodium hydroxide is obtained by passing electricity through an aqueous solution of NaCl(called Brine) which decomposes to form sodium hydroxide. This process is also called Chloro-alkaliprocess because of the product formed chlorine gas and sodium hydroxide.
2NaCl + 2H2O electricity 2NaOH + Cl2 + H2
Properties of Caustic SodaSOME IMPORTANT COMPOUNDS
1. COMMON SALT
Chemical name: Sodium chlorideChemical formula: NaCl
Formation: Common salt is obtained from sea water by the process evaporation. At some places it is mined from salt rocks.
Properties of Common Salt
(i)Common salt absorbs moisture from atmosphere due to the presence of small amount of magnesium chloride.
(ii) It is thermally stable.
(iii) It is soluble in water.
(iv) It can conduct electricity in aqueous solution.
Uses of common Salt
(i) Common salt is used in cooking purpose.
(ii) It is used as preservative for meat and fishes.
(iii)It is used in manufacturing of soaps.
(iv) It is also used in formation of other compounds like Caustic soda, washing soda, baking soda etc.
2. CAUSTIC SODA
Chemical name: Sodium hydroxideChemical Formulae: NaOH
Formation: Sodium hydroxide is obtained by passing electricity through an aqueous solution of Sodium chloride (Called Brine0), which decomposes to form sodium hydroxide. This process is also called Chloro-Alkali process.
2NaCl + 2H2O ——-🡪 2NaOH + Cl2 + H2
Properties of sodium hydroxide
(i) NaOH is a white crystalline solid.
(ii) NaOH reacts with acids to form salt and water.
NaOH + HCl —-🡪NaCl + H2O
(iii) NaOHreacts with CO2 present in atmosphere to form salt and water.
2NaOH + CO2 ——-🡪 Na2CO3 + H2O
Uses of caustic soda
(i) It is used in making soaps and detergents.
(ii) It is used in making artificial textile fibres.
(iii) It is used in the manufacturing of papers.
(vi) It is also used in oil refining and making dyes.
3. BLEACHING POWDER
Chemical name : Calcium oxy chloride Chemical formula: CaOCl2
Formation: Bleaching powder is obtained by the action of chlorine gas on dry slaked lime
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 CaOCl2 + H2O
Properties of Bleaching powder
(i) Bleaching powder is a yellowish white powder.
(ii) It gives a strong smell of chlorine.
(iii) It react with CO2 present in atmosphere to form calcium carbonate and chlorine gas.
CaOCl2 + CO2 CaCO3 + Cl2
(iv) It react with dilute acids to form salt, water and chlorine gas.
CaOCl2 + H2SO4 CaSO4+ H2O + Cl2
Uses of Bleaching powder
- Bleaching powder is used as an oxidizing agent.
- It is used to clean water.
- It is used in the formation of chloroform.
- It is used for bleaching purpose in textile industries, paper industries and in laundry.
4. WASHING SODA
Chemical name: Sodium carbonate decahydrate Chemical formula: Na2CO3. 10 H2O
Formation: It is obtained by a two step process
1. First of all carbon dioxide gas is passed through brine solution saturated with ammonia to gives precipitate of sodium bicarbonate.
NaCl + H2O + NH3 + CO2 NaHCO3(ppt) + NH4Cl
2. Now the precipitated sodium bicarbonate is filtrated and dried and is ignited to give sodium carbonate.
NaHCO3 Heat Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
Na2CO3 + 10H2O Na2CO3. 10 H2O
(Washing soda)
Properties of Washing soda
- Sodium carbonate is a transparent crystalline solid. It consist of 10 molecule of water of crystallization.
- It is readily soluble in water(on heating).
- When crystals of washing soda are left open in air, they loss 9 molecules of water to form a white powder of sodium carbonate monohydrate.
Na2CO3. 10 H2O Air Na2CO3.9 H2O+ H2O
- On heating, washing soda does not decompose but it losses all of its water molecules of crystallization to form anhydrous salt called soda ash.
Na2CO3. H2O Heat Na2CO3+ H2O
(Soda ash)
Or
Na2CO3. 10 H2O Heat Na2CO3 + 10 H2O
(soda ash)
Uses of Washing Soda
- It is used for washing clothes.
- It is used to remove hardness of water.
- It is used in manufacturing of detergents.
- It is used in paper and paint industries.
- It is used as cleansing agent for domestic purpose.
5.BAKING SODA
Chemical name: Sodium bicarbonateChemical formula:NaHCO3
Formation:Sodium bicarbonate is obtained by saturating a cod solution of sodium carbonate with Carbon dioxide. Being less soluble in water sodium bicarbonate is separated as white crystals.
Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2 2NaHCO3
(Sodium carbonate) (Baking soda)
Properties of Baking Soda
- Sodium bicarbonate is a white crystalline solid.
- It is readily soluble in water and its aqueous solution is alkaline in nature.
- It is a non corrosive base.
- On heating, Sodium bicarbonate gets converted into sodium carbonate with the evolution of carbon dioxide gas.
2NaHCO3 heating Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
(Baking soda) (Sodium carbonate)
Uses of Baking Soda
(i) Baking soda is used in the formation of baking powder.
(ii) It is used in fire extinguishers.
(iii) It is also used as an antacid.
Q: What is a baking powder?
Ans: Baking powder is mixture of sodium bicarbonate and an acidic compound such as citric acid.
6. PLASTER OF PARIS
Chemical name: Calcium sulphatehemihydrateChemical Formula: CaSO4. ½ H2O
Formation:plaster of paris is obtain by heating Gypsum [CaSO4. 2H2O]at 120oC to 125oC
CaSO4 . 2H2O Heating CaSO4. ½ H2O+ 3/2 H2O
( Gypsum) (POP)
Properties of POP
- It is a white powder.
- It absorbs water evolution of heat.
- When it is mixed with water, it form a paste which set into a hard mass.
Uses of POP
- It is used to make statue, toys and decorating objects.
- It is used for making black board chalk.
- It is used in plastering fractured bones.
- It is used for sealing air gaps.
AMPHOTERIC OXIDE
The oxides of metals which shows both acidic as well as basic nature are known as amphoteric oxide. Such metallic oxide react with acids as well as base to produce salt and water.
Example: Aliminium oxide and zinc oxide
Q: You have been provided with three test tubes one of them contains distilled water and other two contain an acidic and a basic solution respectively. If you are given only red litmus paper, how will you identify the content of each test tube?
Ans: 🡺First of all mark the three test tubes as A,B and C.
🡺A drop of solution A is put on red litmus paper and same is repeated with solution B and solution C. If either of them turns the litmus paper to blue then it is basic.
🡺 Therefore out of three one is eliminated, now a drop of basic solution is added to both the remaining solutions separately.
🡺Now check the nature of both the mixtures by using red litmus paper.
🡺The mixture that turn the litmus paper to blue is distilled water and the remaining is an acid.
