CLASS-10
CHAPTER-8
HOW DO ORGAISMS REPRODUCE?
REPRODUCTION
The production of new organism from the existing organism of the same species is called reproduction. Reproduction is essential for the survival of species on this earth. The process of reproduction ensure continuity of life on earth. Reproduction give rise to more organism with the same basic characteristics as their parents.
Q:What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction?(Ncert page:128).
Ans: The DNA (Deoxyribo nucleic acid) molecules in the chromosomes in the nucleus is responsible for the transfer of characters from the parents to the off springs. During reproduction the reproductive cells produce two copies of the DNA which separate into two cells. The DNA copies will be similar but not identical to each other. So the new individuals have slight variations from their parents. This is the basis for variations and evolution of new species.
Q: What are the importance of variations?
Ans: Variations during reproduction is important for maintaining the body designs of different organisms to survive in the existing environment. But the environment is constantly changing due to changes in temperature, climate, water levels etc. If organisms cannot adjust themselves to the changes in the environment then their species will become extinct. If there are variations in some individuals of a species they may be able to survive the changes in the environment. So variations in species is necessary for the survival of different species and for the evolution of new species.
Q:Why is variation beneficial to the species but not necessarily for the individual?(Ncert page:128)
Ans: Variations are beneficial to the species than individual because sometimes for a species, the environmental conditions changes so drastically that their survival become difficult. For example- if the temperature of water increases suddenly, then most of the bacteria living in that water would die. Only few variants that are resistant to heat would be able to survive, if these variants were not there, then entire species of bacteria would have been destroyed.
Thus, these variants help in the survival of the species. However, all variations are not necessarily beneficial for the individual organisms.
TYPES OF REPRODUCTION
There are two main methods of reproduction in living.
- Asexual reproduction.
- Sexual reproduction.
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION: The production of new organism from a single parent without the involvement of sex cells (or gametes) is called asexual reproduction.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION: The process of production of new organism from two parents by making use of sex cells.
METHODS OF ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION :It takes place by 6 methods.
- Fission
- Budding
- Spore formation
- Regeneration
- Fragmentation
- Vegetative Propagation
(1) FISSION
In the process of fission a unicellular organism split to form two or more new organism. It is of two types.
(a) Binary fission: In Binary Fission , the parent organism splits to form two new organisms for example- Amoeba, Paramecium Leishmania, Bacteria etc are reproduce by binary fission.
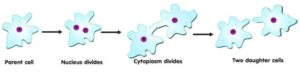
When the amoeba cell has reached its maximum size of growth, then first the nucleus of amoeba lengthen and divide into two parts after that cytoplasm of parent amoeba divides to form two smaller daughter amoeba . In amoeba fission take place in any plane but in Leishmania splitting of parent cell during fission takes place in definite place longitudinal with respect to flagellum at its end.
(b) Multiple Fission: In multiple fission the parent organism splits to form many new organisms at same time. For example: Plasmodium.
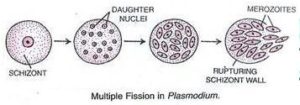
Some organisms (like plasmodium) during unfavorable condition a cyst or protective wall is formed around the cell. Inside the cyst the nucleus of cell splits several time to form many daughter nuclei and then cytoplasm collect around each daughter nuclei and thin membrane are form so many new daughter cells are form with in a cyst. When a favorable conditions arrive the cyst breaks open and daughter cells are released each forming a new organism.
(2) BUDDING
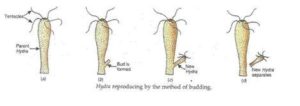
In budding a small part of a body of parent organism grows out as a bud which then detaches and become a new organism.
For Example: Hydra, yeast reproduce by budding.
In Hydra a small out growth (bud) is formed on the sites of its body by the repeated division of its cell. This bud then grows gradually by developing mouth and tentacles and then tiny new hydra detaches itself from parent organism and lives as a separate organism.
(3) SPORE FORMATION:
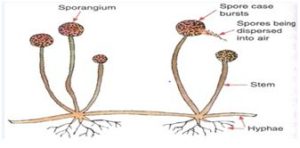
In spare formation, the parent plant produces 100 of microscopic reproductive units called “spores” with in the spore case. When the spore case burst, then the spores spread into air. When these air borne spores land on food or soil, under favorable condition they germinate and produce new plants for example: Most of the fungi such as Rhizopus ( bread mould) ,mucor, bacteria, non-flowering plants, ferns and mosses.
The common bread mould plant (Rhizopus) consists of thread like hyphae and thin stretch having knob like sporangium which contains 100 of spores enclosed in spore-case. When the spore case burst, then the spores spread into air. When these air borne spores land on food or soil, under favorable condition they germinate and produce new plants.
(4) REGENERATION
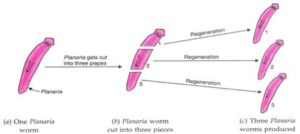
The process of getting back off full organism from its body part is called regeneration. For example simple animals like Hydra and Planaria show regeneration.
Planaria (Flatworm) is found in freshwater ponds. If the body of Planaria some how gets cut into number of pieces then each body piece can regenerate into complete Planaria.
it occurs by the process of growth and development. The cells of cut body part divide rapidly to make ball of cells. The cells present in ball of cells move to their proper places and form various organs and body parts of an organisms.
Q:Why multicellular complex organism cannot show power of regeneration?
In multicellular complex organism, specialized cells makes up tissue, tissue makes up organ, organ makes up organ system and finally organ system makes up organism. They have a high degree of organization in their body so they cannot reproduce their body through regeneration.
Q:How will an organism benefited if it reproduce through spores?
The reproduction by spores take place in plants. Spores are covered by hard protective coat which enables them to survive under unfavorable conditions, like lack of food, lack of water and extreme temperature but when the conditions are favorable the spores can grow to produce new plants. Thus, the reproduction by spores benefits the plant because by surviving under adverse conditions, the spores make these plants live forever.
(5) FRAGMENTATION
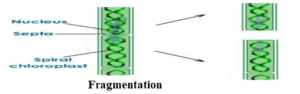
In this method the body of a simple multicellular organism breaks up into smaller pieces on maturation and each fragment develops into new individuals.
Spirogyra is a green filamentous algae. Spirogyra breaks into two or more fragments on maturing and each fragment then grows into new spirogyra.
(6) VEGETATIVE REPRODUCTION(Vegetative propagation):
In this method new plants are produced from the vegetative parts of the plant like root, stem or leaf.
Eg:- (i)from roots – dhalia, sweet potato,
(ii)from stem – potato, ginger
(iii) from leaf – bryophyllum, begonia.
Plants produced by vegetative propagation produce flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds. It also helps in the
propagation of plants which do not produce seeds like rose, jasmine banana etc.
Vegetative propagation can also be done artificially by cutting, layering, grafting etc.

Cutting:
A small part of plant which is removed by making a cut with sharp knife is called cutting. A cut may be a piece of stem, root or leaves. For example-The plant like rose, sugarcane, cactus are grown by cutting. It is necessary that there are some buds on it.
Layering:
In this method a branch of plant is pulled towards the ground and a part of it is covered with moist soil leaving the tip of branch exposed above the ground. after some time new roots develop and then it cut off from parent plant and grows as new plant. for example- Jasmine, strawberry, hibiscus and guava etc.
Grafting:
It is the method in which the cut stem of two different plant one with root and other without root and joined together in such a way that the two stem joint and grows as a single plant. This new plant has the characteristics of both the plants.
The cut stem of plant having root is called stock and the cut stem of another plant is called scion. For example- Apple, peach, apricot, pear etc.
Advantages of vegetative propagation:
- The new plant produced by artificial vegetative propagation are identical to the parent plant.
- The fruit trees grown from cutting or grafting start to bear fruits much earlier.
- Many plants can be grown from just one parent plant.
- We can also get seedless plant by artificial propagation like banana.
TISSUE CULTURE (Micro propagation):
The production of new plants from a small piece of plant tissue removed from a growing tip of plant in a suitable growth medium (culture or jelly like synthetic medium) is called tissue culture.
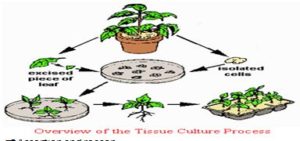
Procedure:
- The tissue is placed on a culture medium which contain nutrients and plant hormones, which make the cells in the plant tissue to divide rapidly to form callus.
- This callus is transfer to another medium containing plant hormone which stimulates the callus to develop roots.
- Then it is put on another medium containing another plant hormone which stimulates the development of shoot.
- The plantlets are then transplanted into soil where they can grow to form mature plant. This technique is used to the production of ornamental plants like orchids, carnation etc.
Advantages:
- It is a very fast technique.
- New plant produced by tissue culture are disease free.
- Very little space is needed.
- By this method plants can be grown around the year irrespective of weather or seasons.
SEXUAL REPTRODUCTION
The process of reproduction from two parents is called sexual reproduction. In this method of reproduction male and female gametes are fuse together to form zygote. Now this zygote developed into new organism.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS
- The plants in which the sex organs are carried within the flowers and the seeds are enclosed in a fruit are called angiosperms (flowering plants).
- The flowering plants are reproduced by sexual reproduction method.
- The function of a flower is to make male and female gametes and to ensure that fertilisation will take place to make new seeds for the reproduction of plant.
(a)REPRODUCTIVE PARTS OF A FLOWERING PLANT
The main parts of flower are:
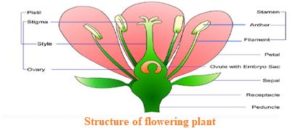
1. STAMEN: Stamen is male reproductive parts of a flowering plant which consist of two parts Anther and Filament.
- Anther: Swollen top of the stemen is called anther. It is responsible to produce pollen grain.
- Filament: Filament is the stalk of the anther which is responsible to hold the anther.
2.PISTIL(Carpel): Pistil is the female reproductive part of the flowering plant which consist of three parts. They are Stigma, style and Ovary.
- Stigma: The top of the pistil is called stigma. It is sticky in nature. It is responsible to receive pollen grain from anther.
- Style: It is the middle part of the pistil It is a tube like structure which is responsible to carry pollen grain from stigma to ovary.
- Ovary : The swollen bottom part of the pistil is called Ovary. It contains ovules and each ovule contains an egg cell.
3.SEPALS(group name calyx): Sepals are green outermost leaf-like floral organs which protect the flower in the bud stage.
4.PETALS(group name corolla):The colorful parts of a flower are called petals. The petals lie inside the sepals.
Q: What do you understand by unisexual and bisexual flowers?.
Ans: Unisexual Flower: The flowers which contain only sex organ, either stamens or carpels are called unisexual flower. For example: papaya and watermelon plants
Bisexual flowers: The flowers which contain both the sex organs, stamens as well as carpel, are called bisexual flowers. For example: Hibiscus and mustard plants.
(b) POLLINATION
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a stamen to the stigma of a carpel is called pollination. Pollination is done by insects, birds, winds and water. There are two types of pollination.
(a)Self-pollination
(b)Cross pollination
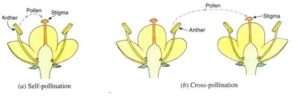
(a)Self-pollination: If the transfer of pollen occurs in the same flower or another flower on the same plant, it is called self-pollination.
(b)Cross pollination:If the pollen is transferred from the anther of a flower on one plant to the stigma of a flower on another similar plant, it is called cross-pollination.
(c)FERTILISATION
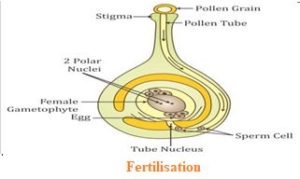
After the pollen grain is transferred to the stigma it produces a pollen tube which passes through the style and enters the ovary and ovule. In the ovule the male germ cell (male gamete) fuses with the female germ cell (female gamete) to form a zygote. This process is called fertilisation.
After fertilisation the zygote divides several times and forms the embryo which then develops into the seed and the ovary develops into the fruit.
REPRODUCTION IN HUMAN BEINGS
(a)MALE REPRODUCTIVE PARTS
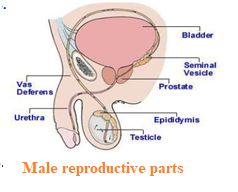
1.TESTES: Male reproductive system consist of a pair of testes located inside scrotum. They are responsible to produce hormone testosterone and regulate the production of sperm.
2. SCROTUM: It is a bag like structure which is responsible to hold the testes and to maintain the sperm temperature less than the body temperature.
3.EPIDIDYMIS: It is a coiled tube like structure and is responsible to store the sperm. Sperm become mature inside the epididymis
4. VAS DEFERENS: It is a tube like structure arise from epididymis and is responsible to carry sperm from epididymis to Urethra.
5. URETHRA: It is a tube like structure arise from Urinary bladder. It is a common passage of urine and sperm both but one at a time.
6. SEMINAL VESICLES AND PROSTATE GLAND: These glands add their secretion to sperm so that sperm become a liquid. This liquid is called semen.
7.PENIS: It is a muscular organ which is responsible to discharge sperm from male body.
(b) FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE PARTS
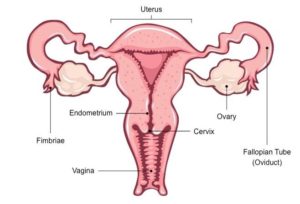
1.OVARIES: Female reproductive system consists of a pair of oval shaped organ known as ovaries. They are responsible to produce ova or egg and female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone.
2. OVIDUCTS( Fallopian tube): it is a tube like structure. it consists of a funnel shaped opening over the each Ovary. The egg released by the ovary goes into the oviduct through funnel shaped opening. Fertilization is also takes place in oviduct.
3. UTERUS: It is a bag like structure connected to each Ovary. The growth and development of fertilized egg takes place in uterus.
4.CERVIX: Cervix is a small opening which is responsible to connect the uterus to vagina.
5.VAGINA: It is a muscular organ which is responsible to receive male reproductive cells(sperm).
(c) FERTILASATION IN HUMAN BEING
During sexual intercourse the sperms from the male enters into the vagina of the female. The sperms reaches the oviduct. One sperm fuses with an egg and forms a zygote. The zygote then gets implanted in the uterus. The zygote then starts dividing to form an embryo. The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood through the placenta. The development of the child takes nine months and then the child is born.
PUBERTY
The time between the childhood and the adulthood is called adolescence.
The age at which sex hormones begin to produced and boy and girls become sexually mature is called puberty.
Puberty ages
In Boys: 13-14 years
In Girls: 10-12 years
COMMON CHANGES IN BOYS AND GIRLS AT PUBERTY
(i)Hairs grows under armpit and in genital area.
(ii)Skin become oily and develop pimple.
(iii) Thinner hair appear on arms and legs.
CHANGES IN BOYS AT PUBERY
(i) Hair grow on face and chest.
(ii)Body become muscular.
(iii) Chest and shoulder become broad.
(iv) Testes began to produce sperms
CHANGES IN GIRLS AT PUBERTY
(i)Brest develop and become enlarged.
(ii)Extra fats are deposited in various parts of the body like hips and thigh.
(iii) Fallopian tube become enlarged.
(iv) Menstruation become starts.
MENSTRUATION
The ovary produces one egg every month and the uterus prepare to receive fertilized egg. Its wall becomes thick and spongy with blood vessels for nourishing the embryo. If fertilization does not take place then the uterus wall breaks and comes out of the vagina as blood and mucous. This cycle takes place every month and called menstruation.
