CLASS-X
CHAPTER-5
PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS
CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS
The method of placing elements into different groups on the basis of similarities in their properties is called classification of elements. Classification makes the study of elements easier.
Note: There are about 114 different elements known so far.
LAVOISIER’S CLASSIFICATION (in 1789)
It is the earliest classification of elements in which Lavoisier divided the elements into two groups called metals and non-metals.
- The elements which have the tendency to lose electrons are called metals.
- The elements which have the tendency to gain electrons are called non-metals.
At that time, there were only about 30 known elements.
DRAWBACKS
OF LAVOISIER’S CLASSIFICATION
The main
drawback of this classification was that it had no place for metalloids which
were discovered later.
DOBEREINER’S CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS (in 1817)
Johann
Wolfgang Dobereiner classified elements in the increasing order of their
atomic masses into groups of three elements called triads. In each
triad, the atomic mass of middle element was approximately equal to the average
atomic mass of other two elements.
For Example
|
Triads |
Atomic mass |
Average atomic mass of 1st and 3rd element |
|
Lithium Li Sodium Na Potassium K |
6.9 23 39 |
(6.9+39)/2= 22.95 |
|
Calcium Ca Strontium Sr Barium Ba |
40.1 87.6 137.3 |
(40.1+137.3)/2= 88.7 |
|
Chlorine Cl Bromine Br Iodine I |
35.5 79.9 126.9 |
(35.5+ 126.9)= 81.2 |
DRAWBACKS
OF DOBEREINER TRIADS
èAll the elements
discovered at that time could not be classified into triads. Dobereiner could
identify only three triads .He was not able to prepare triads of all the known
elements.
èFor very low or for
very high mass elements, the law was not holding good. For example F, Cl and Br. The atomic mass of Cl is
not equal to the atomic masses of F and
Br.
3.
NEWLAND’S CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS(Newland‘s low of octaves) in 1866
John
Newland arrange the elements in the increasing order of their atomic masses
into groups of 8 elements called octaves like musical notes. Now he
found that when the elements were arranged in the increasing order of their
atomic masses into octaves, then there was a similarity of properties in every
8th elements.
For example
|
Sa |
Re |
Ga |
Ma |
Pa |
Da |
Ni |
|
H |
Li |
Be |
B |
C |
N |
O |
|
F |
Na |
Mg |
Al |
Si |
P |
S |
|
Cl |
K |
Ca |
Cr |
Ti |
Mn |
Fe |
|
Co & Ni |
Cu |
Zn |
Y |
In |
As |
Se |
|
Br |
Rb |
Sr |
Cl & La |
Zr |
– |
– |
DRAWBACKS
IN NEWLAND’S OCTAVES
1.
All the elements discovered later could not be correctly arranged into octaves.
2.
Some elements having different properties were placed in same group.
For
example- Cobalt and Nickel having different properties from chlorine,
fluorine and bromine but are placed in same group.
3.
Some elements having similar properties were placed in different group.
For
example- Cobalt and Nickel have same properties as Iron but
were placed in different groups.
Q1. Did Dobereiner’s triads also exist in the columns of Newlands’ Octaves? Compare and find out.( Page No: 81 NCERT)
Ans: Yes, Dobereiner’s triads also exist in the columns of Newlands’ Octaves. One such column is Li, K, Na.
Q 2 What were the limitations of Dobereiner’s classification? .( Page No: 81 NCERT)
Q 3. What were the limitations of Newlands’ Law of Octaves? .( Page No: 81 NCERT)
4.MENDELEEV’S PERIODIC TABLE (1834-1907)
Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev classified the elements on the following basis:-
- He arranged the elements in the increasing order of their atomic masses and similarities in their properties.
- The formulae of oxides and hydrides formed by the elements was also the basis for the classification of elements.
STRUCTURE OF MENDELEEV’S PERIODIC TABLE
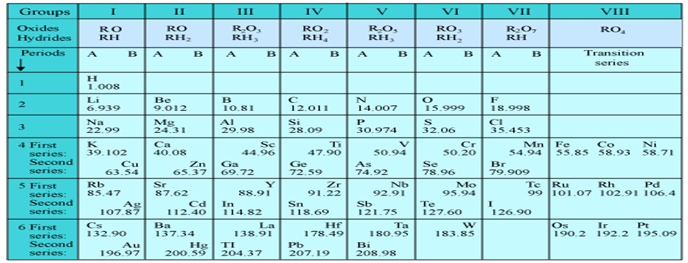
1. Mendeleev’s periodic table has 6 horizontal rows called periods and 8 vertical rows called groups.
2. The group 1 to 7 are divided into two subgroups called subgroup-A and subgroup-B.
3. Group 8 is divided into three vertical rows of elements.
4. Elements having similar properties were placed in same group.
5. There are some spaces left vacant in the table to place the elements to be discovered later.
MERITS OF MENDELEEV’S PERIODIC TABLE
1. In mendeleev’s periodic table, elements were arranged on more fundamental basis of their atomic masses and properties.
2. Some space were left vacant to accommodate the elements to be discovered later.
3. It could predict the properties of elements which help in the discovery of new elements.
4. The inert gases discovered later could be placed in a separate group without disturbing the table.
DRAWBACKS’S OF MENDELEEV”S PERIODIC TABLE
1. Some elements were not arranged in the increasing order of their atomic masses.
For example: Co is placed before Ni and Te is placed before I
2. Position of hydrogen is not clear because it shows properties similar to metals of group A as well as non-metals of group-7.
3. The positions of Isotopes were not clear.
4. It does not give the information about the electronic configuration of elements.
NOTE: An element discovered later Md(Mendelevium) named on the name of Mendeleev.
NOTE: (a) Eka-Aluminium(one place before aluminium)—> Similar to Gallium
|
Properties |
Eka-aluminium |
Gallium |
|
Atomic mass |
68 |
69.72 |
|
Formula of oxide |
E2O3 |
Ga2O3 |
|
Formula of chloride |
ECl3 |
GaCl3 |
(b) Eka- Silicon–> Similar to Germanium
|
Properties |
Eka- Silicon |
Germanium |
|
Atomic mass |
72 |
72.6 |
|
Formula of oxide |
EO2 |
GeO2 |
|
Formula of chloride |
ECl4 |
GeCl4 |
Q 1. Use Mendeleev’s Periodic Table to predict the formulae for the oxides of the following elements: K, C, Al, Si, Ba. (Page No: 85 NCERT)
Answer
K is in group 1. Therefore, the oxide will be K2O.
C is in group 4. Therefore, the oxide will be CO2 .
Al is in group 3. Therefore, the oxide will be Al2O3 .
Si is in group 4. Therefore, the oxide will be SiO2 .
Ba is in group 2. Therefore, the oxide will be BaO.
Q 2. Besides gallium, which other elements have since been discovered that were left by Mendeleev in his Periodic Table? (any two) (Page No: 85 NCERT)
Answer Scandium and germanium.
Q 3. What were the criteria used by Mendeleev in creating his Periodic Table? (Page No: 85 NCERT)
Answer Mendeleev used atomic mass of the elements as the unique criteria of the elements. He proposed that the chemical properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic masses. And thus, he arranged the elements in the increasing order of their atomic masses.
Q 4. Why do you think the noble gases are placed in a separate group? (Page No: 85 NCERT)
Answer Noble gases are inert elements. Their properties are different from the all other elements. Therefore, the noble gases are placed in a separate group.
MODERN PERIODIC TABLE
In modern periodic table, elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic numbers in the form of a table having seven horizontal rows of elements called ‘periods’ and 18 vertical rows of elements called ‘groups’.
(a)PERIODS
There are 7 periods in the modern periodic table.
(i) First period has two elements H and He and is called very short period.
(ii) Second period has 8 elements Li to Ne and is called short period.
(iii) Third period has 8 elements Na to Ar and is called short period.
(iv) Fourth period has 18 elements K to Kr and is called long period.
(v) Fifth period has 18 elements Rb to Xe and is called long period.
(vi) Sixth period has 32 elements from Cs to Rn and is called very long period.
(vii) Seventh periods has 28 elements from Fr to atomic number 114 and is called incomplete period.
14 elements each of 6th and 7th period are placed separately at the bottom of the table and are called Lanthanides and Actinides.
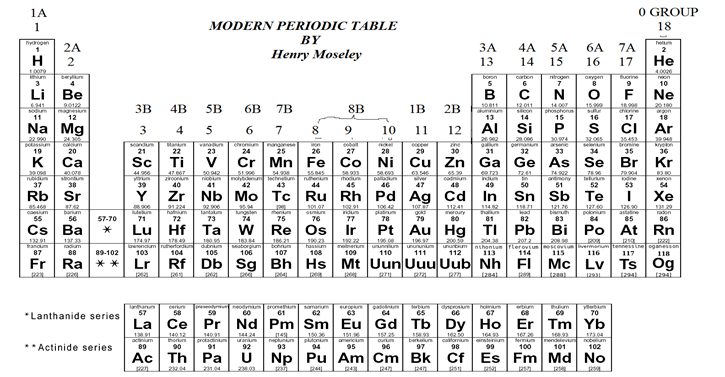
(b) GROUPS
There are 18 Groups of elements divided into 9 main Group. They are I , ii, iii, iv , v, vi, vii, viii and 0 Group. The groups 1 to 7 has two subgroups called subgroup-A and subgroup-B. Group 8 has three rows of elements and 0 Group has one row of elements.
(i) The elements of A-subgroup are called normal elements.
(ii) The elements of B-subgroup are called transition elements.
(iii) Group 1 (1A) elements are called alkali metals.
(iv) Group 2(2A) elements are called alkaline earth metals.
(v) Group 17(7A) elements are called halogens.
(vi) Group18(0 Group) elements are called noble gases or inert gases.
Note: (a) The number of valance electrons in the electronic configuration of an elements represent the group number of that element..
(b) The number of shells in the electronic configuration of an element represents the Period of that element.
PROPERTIES OF ELEMENTS IN PERIODS AND GROUP
1. VALANCE ELECTRONS
(a)IN PERIODS: In a period the number of valance electrons increases from 1 to 8 on going left to the right but the number of shells remain same.
Eg : Second group
|
Elements |
Li |
Be |
B |
C |
N |
O |
F |
Ne |
|
Atomic no |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
E.C |
2,1 |
2,2 |
2,3 |
2,4 |
2,5 |
2,6 |
2,7 |
2,8 |
|
V.E |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
No of Shells |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
(b) IN
GROUPS: In a group, the number of valance electrons is the same for all the
elements but the number of shells increases from top to bottom.
Eg: Group 1 (IA)
|
Elements |
Atomic no |
E.C |
V.E |
No of Shells |
|
H |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
Li |
3 |
2,1 |
1 |
2 |
|
Na |
11 |
2,8,1 |
1 |
3 |
|
K |
19 |
2,8,8,1 |
1 |
4 |
(a)IN PERIOD
Eg: Second Period
|
Elements |
Li |
Be |
B |
C |
N |
O |
F |
Ne |
|
Atomic no |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
E.C |
2,1 |
2,2 |
2,3 |
2,4 |
2,5 |
2,6 |
2,7 |
2,8 |
|
V.E |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
No of Shells |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
When we move in a period from left to right, the valency of elements increases from 1 to 4
and then decreases from 4 to 0.