EKUL EDUCATION
CLASS-10
CHEMICAL EQUATIONS AND REACTIONS
CHEMICAL REACTION: A chemical reaction is a chemical change in which one or more substances react to form new substances with entirely different properties.
For example-Respiration, burning of fuel, Rusting of iron, photosynthesis, Digestion of food etc.

REACTANTS AND PRODUCTS
REACTANTS-The substances that take part in a chemical reaction are known as reactants.
PRODUCTS- The new substances formed during a chemical reaction are known as products.
For example-
Hydrogen + Oxygen ——> Water
Here, Hydrogen and oxygen takes part in the chemical reaction and are known as reactants and water is the new substance formed and is known as product.
Q: How can you identify a chemical reaction (or chemical change)?
Ans: A chemical change can be identified by
(i) Change in colour
When Iron nail is placed in copper sulphate solution then blue colour copper sulphate is changes into green colour ferrous sulphate solution.
(ii) Evolution of gas.
Sodium metal react with sulphuric acid then hydrogen gas is evolved along with the formation of sodium sulphate.
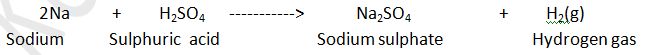
(iii)Change in temperature.
When water is added to calcium Oxide(Quick lime) , a lots of heat is evolved along with the formation of calcium hydroxide(slaked lime).
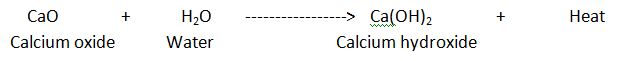
(iv)Change in state.
Hydrgen and Oxygen react to form water.

(v) Formation of precipitate
When barium chloride react with sodium sulphate then white ppt of barium sulphate is formed.

CHEMICAL EQUATION
A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction in which substances are represented by their chemical formulae.
For example– Chemical equation of burning of methane can be written as
CH4 + 3O2 ————-> CO2 + 2H2O
Methane Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water
Q: How can you convert a word equation in chemical equation?
Ans: A word equation can be changed in a chemical equation by writing symbols and formulae of substance in place of their names.
For example-
Word Equation:
Calcium oxide + water ——- > Calcium hydroxide + Energy
Chemical Equation:
CaO + H2O ————> Ca(OH)2 + Energy
TYPES OF CHEMICAL EQUATIONS
There are two types of chemical equations. They are balanced and un balanced Chemical reactions.
(a) BALANCED CHEMICAL EQUATIONS : A chemical equation is said to be balanced if the total number of atoms of each elements are same in reactants and products.
For Example-
C + O2 —————- > CO2
Here, total number of carbon and oxygen atoms are same in reactants and products. Hence, it is a balanced chemical equation.
(b)UNBALANCED CHEMICAL EQUATIONS: A chemical equation is said to be unbalanced if the total number of atoms of each elements are not same in reactants and products.
For Example-
H2 + O2 ————-> H2O
Here , number of hydrogen atoms are same in reactants and products but the number of oxygen atoms are not same in reactants and product. Hence it is not an unbalanced chemical equation.
Q: What is the need to balance a chemical equation?
Ans: We need to balance a chemical equation to satisfy the law of mass conservation according to which total mass of reactants is always equal to the total mass of products.
Q: Balance the following chemical equations?
(a) H2 + O2 ——-> H2O
(b) Fe + H2O ——–> Fe2O3 + H2
(c) Fe2O3 + C ———–> Fe + CO2
(d) HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 —————-> Ca(NO3)2 + H2O
(e) NaOH + H2SO4 —————-> Na2SO4 + H2O
(f) CO2 + H2O —————> C6H12O6 + O2
Ans:
(a) 2H2 + O2 ——-> 2H2O
(b) 4 Fe + 3H2O ——–> 2Fe2O3 + H2
(c) 2Fe2O3 + 3C ———–> 4Fe + 3CO2
(d) 2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 —————-> Ca(NO3)2 + H2O
(e) 2NaOH + H2SO4 —————-> Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(f) 6CO2 + 6H2O —————> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Q: How Can you make a Chemical equation more informative?
Ans: We can make a chemical equation more informative in the following ways
1.By Writing the name of the substances
2.By writing the physical state of the substances
Solid state can be represented by symbol (s)
- Liquid state can be represented by symbol (l)
- Gas state can be represented by symbol (g)
- Aqua solution can be represented by symbol (aq)
3.By writing the conditions in which a chemical reaction takes place like temperature, pressure, sunlight etc.
4.By representing the precipitation by symbol (ppt) ) or
5.By writing the catalyst if used.
For Example- Sunlight
6CO2 (g) + 6 H2O(l) —————-> C6H12O6 (s) + 6O2 (g)
Chlorophyll
Q: What are the importance’s of chemical equation?
Ans: Some of the importance of chemical equation are
1.It informs about the symbols and formulae of the substances involving in the chemical reaction.
2It informs about the physical states of the substances.
3.It ensure that the number of atoms of each elements are equal in reactants and products.
Q:Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air?[Ncert page no-6]
Ans :Magnesium ribbon must be cleaned with sand paper so that the layer of magnesium oxide layer(which is formed due reaction of magnesium with air) can be removed in order to remove desired reaction.
2.Write the balanced equation for the following chemical reactions.[Ncert page no-6]
(i) Hydrogen + Chlorine —————-> Hydrogen chloride
Ans: H2 + Cl2 —————> 2HCl
(ii)Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate ——–> Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
Ans: 3 BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 ———–> 3BaSO4 + 2AlCl3
3.Write a balanced chemical equation with state symbols for the following reactions.
(i) Solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble barium sulphate and the solution of sodium chloride.
Ans: BaCl2 + Na2SO4 —————-> BaSO4 + 2NaCl
Barium Sodium Barium Sodium
Chloride sulphate sulphate(white ppt) chloride
(ii) Sodium hydroxide solution (in water) reacts with hydrochloric acid solution (in water) to produce sodium chloride solution and water.
Ans NaOH + HCl —————-> NaCl + H2O
Sodium Hydrochloric Sodium Water
hydroxide acid chloride
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
There are mainly four types of chemical reactions. They are
(i) Combination reactions
(ii)Decomposition reactions
(iii)Single Displacement reaction
(iii) Double displacement reactions
(i)COMBINATION REACTIONS:A reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a single produce is called combination reaction.
General form:
A + B ————> C
For Example:
(a) Burning of Coal: Carbon combines with oxygen to form Carbon dioxide.
C + O2 ————–> CO2
(b) Oxygen combines with oxygen to form water
2H2+ O2 ————-> 2H2O
(c) When sulphur burns in air then it combines with air to form sulphur dioxide.
S + O2 ————> SO2
(d) Nitrogen combines with hydrogen to form ammonia.
N2 + 3H2 ———–> 2NH3
(e) When magnesium ribbon burns in air then it combines with oxygen to form a layer of magnesium oxide over it.
Mg + O2 ———-> MgO
(ii)DECOMPOSITION REACTIONS: A reaction in which a single reactant break to form two or more products is called decomposition reaction. This reaction is just opposite to the combination reaction.
General form:
AB ————–> A + B
For Example :
Heat
CaCO3 ————–> CaO + O2
TYPES OF DECOMPOSITION REACTION: On the basis of the type of energy used to break the reactant molecule, decomposition reactions are classified as-
(i) Thermal decomposition reaction
(ii)Photolytic decomposition reaction
(iii)Electrolytic decomposition reaction
(i) THARMAL DECOMPOSITION REACTION:
A decomposition reaction in which heat energy is used to break the reactant molecule is called thermal decomposition reaction.
For example:
(i) When Calcium carbonate is heated the it decomposes into calcium oxide and oxygen gas.
Heat
CaCO3 ————-> CaO + O2
(ii) When copper carbonate is heated the it decomposes into copper oxide and oxygen gas.
Heat
CuCO3 ———-> CuO + O2
(ii) PHOTOLYTIC DECOMPOSITION REACTION:
A decomposition reaction in which sunlight is used to break the reactant molecule is called photolytic decomposition reaction.
For example :
(a)When silver chloride is exposed to sunlight then it decomposes into silver metal and chlorine gas.
Sunlight
2AgCl ————-> 2Ag + Cl2
(b)When silver bromide is exposed to sunlight then it decomposes into silver metal and bromine.
Sunlight
2AgBr ————-> 2Ag + Br2
(iii)ELECTROLYTIC DECOMPOSITION REACTION:
A decomposition reaction in which electricity is used to break the reactant molecule is called electrolytic decomposition reaction.
For example:
(a) When electricity is passed through water then it decomposes into hydrogen and oxygen gas
Electricity
2H2O ————-> H2 + O2
(b) When electricity is passed through sodium chloride solution then it decomposes into sodium metal and clorine gas
Electricity
NaCl ———-> 2Na + Cl2
(ii)DISPLACEMENT REACTION/ SINGLE DISPLACEMENT REACTION:
A reaction in which a more reactive element displaces less reactive element from its salt is called displacement reaction or single displacement reaction.
General Form:
A + BC ————> AC + B
For example:
(i) When zinc metal reacts with copper sulphate solution then it displaces copper from copper sulphate and form zinc sulphate. (Here zinc metal is more reactive than copper metal)
Zn + CuSO4 ———-> ZnSO4 + Cu
(ii) When iron metal reacts with copper sulphate solution then it displaces copper from copper sulphate and form iron sulphate. (Here iron metal is more reactive than copper metal)
Fe + CuSO4———-> FeSO4 + Cu
(iii)DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTION:
A reaction in which exchange of ions take place between two reactant molecules to form products is called double displacement reaction.
General form:
AB + CD ———–> AD + CB
For example:
(i) When sodium sulphate is added to barium chloride, white precipitate of barium sulphate and sodium chloride are formed.
Na2SO4 + BaCl2 ———> BaSO4 + 2NaCl
White ppt
(ii) When silver nitrate is added to sodium bromide, yellow precipitate of silver bromide and sodium nitrate are formed.
AgNO3 + NaBr ———>AgBr + NaNO3
Yellow ppt
OXIDATION AND REDUCTION REACTIONS
(a)OXIDATION REACTION:
An Oxidation reaction can be defined as :
- The process in which oxygen is added to a substances.
- The process in which hydrogen is removed from a substances.
- The process in which electrons are released by an atom.
For example:
1.Addition of oxygen takes place
4Na + O2 ———-> 2Na2O
2.Removal of hydrogen takes place
2NH3 ———-> N2 + 3 H2
3.loss of electrons take place
Zn ———> Zn++ + 2e-
(b) REDUCTION REACTION:
An Reduction reaction can be defined as :
- The processes in which hydrogen is added to a substance.
- The processes in which oxygen is removed from a substance.
- The processes in which electrons are gained by a substance.
For example:
1. Addition of hydrogen
N2 + 3H2 ————–> 2NH3
2.Removal of oxygen
2 KClO3 ———> 2KCl + 3O2
3. Gain of electron
Cl + e- ————> Cl–
REDOX REACTION
A reaction in which oxidation and reduction takes place simultaneously is called redox reaction.
For example:
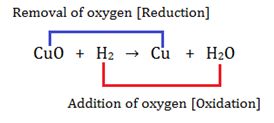
In the above reaction oxygen is removed from copper oxide and it is reduced to copper and oxygen is added to Hydrogen and it is oxidized to water.
Here,
Oxidizing agent- CuO
Substance reduced- CuO
Reducing agent- H2
Substances Oxidised- H2
DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN OXIDISING AND REDUCING AGENT
OXIDISING AGENT | REDUCING AGENT |
1. A substance which help in the oxidation of other substances is called oxidising agent | 1. A substance which help in the reduction of other substances is called reducing agent |
2. It either add oxygen or remove hydrogen from a substance. | 2. It either add hydrogen or remove oxygen from a substance. |
3. It donate electrons to other substances. | 3. It accept electrons from other substances. |
4. Oxidising agent itself gets reduced to oxidise other substances. | 4. Reducing agent itself gets oxidised to reduce other substances. |
EXOTHERMIC AND ENDOTHERMIC REACTIONS
EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS:
A chemical reaction in which heat is evolve along with the formation of products is called exothermic reaction.
For Example:
When water is added to calcium oxide(Quick lime) then alots of heat is evolve along with the formation of calcium hydroxide.
CaO + H2O ——–> Ca(OH)2 + Heat
Some Other examples
Mg + O2 ———-> MgO + Heat
2Al + Fe2O3 ———-> Al2O3 + Fe + Heat
ENDOTHERMIC REACTIONS
A chemical reaction in which energy in provided to reactant molecule in order to form product.
For Example:
When heat energy is provided to calcium carbonate then it breaks into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
Heat
CaCO3 ———–> CaO + CO2
Some other Examples
Sunlight
2AgCl ————–> 2Ag + Cl2
Electricity
2NaCl —————-> 2Na + Cl2
Q: How can we say that respiration is an exothermic reaction ?
Ans: As we know during respiration carbohydrates present in food broken down to form glucose. This glucose combine with oxygen in the cell of our body and produce energy .Since in this process energy is released .Therefore it is known as Exothermic reaction .
RECIPITATION REACTION
Thereaction in which preof the productis obtained in the form of precipitate is known as precipitation reaction .
For Example:
BaCl2+ Na2SO4 ————-> BaSO4 + 2NaCl
barium sodium barium sodium
Chloride sulphate sulphate chloride
White ppt
CORROSOIN
The phenomena due to which metals are slowly eaten by the action of air , water and chemicals present in the atmosphere .
For Example : Most common example of corrosion is rusting of iron .
RUSTING OF IRON
When iron articles are kept in moist place then a layer of iron oxide is formed on it . this process is known as rusting of iron
4Fe + 3O2 + 2H2O ————> 2Fe2O3 . x.H2O
(hydrated iron oxide )
CODITION NECESSARY FOR CORROSION
There are two condition necessary for corrosion
1. presence of air
2. presence of moisture (water)
METHODS TO PREVENT CORROSION OF IRON
1,Corrosion can be prevented by greasing and plastic coating , painting , galvanising (zinc coating ) etc.
2.by using alloys of metals in place of pure metals .
RANCIDITY
It is the process of slow oxidation of oils and the fats present in the food materials resulting in the production of foul smell and taste in them .
METHODS TO PREVENT RANCIDITY
Some of the methods to prevent rancidity are:
1.Packing of the food material in air tight container .
2.Refrigerating of cooked food at low temperature .
3. By adding antioxidants .
4.Avoiding the food materials and cooked food keeping in direct sunlight .
Q: Name any to antioxidants which is usually added to fat and oil containing food ?
Ans : Two common antioxidants are :
- Butylated Hydroxy Anisole (BHA)
- Butyland Hydroxy Toluene (BHT)